- Brain tumors are the second leading cause of childhood cancer deaths, following leukemia.
- Brain tumors are the second most common form of solid tumors among children.
- There are over 28,000 children living with a brain tumor diagnosis in the United States.
- More than 4,000 new cases of childhood primary brain and central nervous system tumors are estimated to occur in 2010. Nearly three-fourths of these new cases will be among children under the age of 15.
- Over 72% of children affected by brain tumors will be long-term survivors.
Brain tumour
Tuesday, 20 September 2011
September is Childhood Cancer Awareness Month
During the month of September, the National Brain Tumor Society (NBTS) is joining national efforts to raise awareness of the unique needs and concerns of childhood cancer survivors. Did you know1:
Friday, 16 September 2011
Information About Brain Tumors
The brain tumor experience can be a journey into an unknown land filled with uncertainty. Gathering information about brain tumors can help you understand your options and, in the process, feel more in control.
The topics in this section will help you better understand brain tumors. Information about the Anatomy of the brain provides insight into the major parts of the brain and what areas might be affected given the location of the tumor. Symptoms and Diagnosis describes the common symptoms of brain tumors as well as the diagnostic tests used to identify tumor type. Brain Tumor FAQ provides answers to frequently asked questions about brain tumors, whereas Ask the Health Professional, Link Library, and Publications offer a wealth of resources to help you learn more about and cope with your diagnosis and treatment. Finally, a comprehensive Glossary will familiarize you with the many medical terms you are sure to encounter.
Saturday, 10 September 2011
Signs and symptoms
The visibility of signs and symptoms of brain tumors mainly depends on two factors: tumor size (volume) and tumor location. The moment that symptoms will become apparent, either to the person or people around him (symptom onset) is an important milestone in the course of the diagnosis and treatment of the tumor. The symptom onset - in the timeline of the development of the neoplasm - depends in many cases on the nature of the tumor but in many cases is also related to the change of the neoplasm from "benign" (i.e. slow-growing/late symptom onset) to more malignant (fast growing/early symptom onset).
Symptoms of solid neoplasms of the brain (primary brain tumors and secondary tumors alike) can be divided in 3 main categories :
When a person suffering from a metastasized cancer is diagnosed, a scan of the skull frequently reveals secondary tumors.
In a recent study by the Dutch GP Association,[1] a list of causes of headaches [2] was published, that should alert GP's to take their diagnosis further then to choose for symptomatic treatment of headaches with simple pain medication (note the occurrence of brain tumors as possible cause) :
Symptoms of solid neoplasms of the brain (primary brain tumors and secondary tumors alike) can be divided in 3 main categories :
- Consequences of intracranial hypertension : The symptoms that often occur first are those that are the consequences of increased intracranial pressure: Large tumors or tumors with extensive perifocal swelling (edema) inevitably lead to elevated intracranial pressure (intracranial hypertension), which translates clinically into headaches, vomiting (sometimes without nausea), altered state of consciousness (somnolence, coma), dilation of the pupil on the side of the lesion (anisocoria), papilledema (prominent optic disc at the funduscopic eye examination). However, even small tumors obstructing the passage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) may cause early signs of increased intracranial pressure. Increased intracranial pressure may result in herniation (i.e. displacement) of certain parts of the brain, such as the cerebellar tonsils or the temporal uncus, resulting in lethal brainstem compression. In very young children, elevated intracranial pressure may cause an increase in the diameter of the skull and bulging of the fontanelles.
- Dysfunction : depending on the tumor location and the damage it may have caused to surrounding brain structures, either through compression or infiltration, any type of focal neurologic symptoms may occur, such as cognitive and behavioral impairment (including impaired judgment, memory loss, lack of recognition, spatial orientation disorders), personality or emotional changes, hemiparesis, hypoesthesia, aphasia, ataxia, visual field impairment, impaired sense of smell, impaired hearing, facial paralysis, double vision, dizziness, but more severe symptoms might occur too such as: paralysis on one side of the body hemiplegia or impairment to swallow . These symptoms are not specific for brain tumors — they may be caused by a large variety of neurologic conditions (e.g. stroke, traumatic brain injury). What counts, however, is the location of the lesion and the functional systems (e.g. motor, sensory, visual, etc.) it affects. A bilateral temporal visual field defect (bitemporal hemianopia—due to compression of the optic chiasm), often associated with endocrine disfunction—either hypopituitarism or hyperproduction of pituitary hormones and hyperprolactinemia is suggestive of a pituitary tumor.
- Irritation : abnormal fatigue, weariness, absences and tremors, but also epileptic seizures.
When a person suffering from a metastasized cancer is diagnosed, a scan of the skull frequently reveals secondary tumors.
In a recent study by the Dutch GP Association,[1] a list of causes of headaches [2] was published, that should alert GP's to take their diagnosis further then to choose for symptomatic treatment of headaches with simple pain medication (note the occurrence of brain tumors as possible cause) :
Brain tumor
A brain tumor is an intracranial solid neoplasm, a tumor (defined as an abnormal growth of cells) within the brain or the central spinal canal.
Brain tumors include all tumors inside the cranium or in the central spinal canal. They are created by an abnormal and uncontrolled cell division, normally either in the brain itself (neurons, glial cells (astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, ependymal cells, myelin-producing Schwann cells), lymphatic tissue, blood vessels), in the cranial nerves, in the brain envelopes (meninges), skull, pituitary and pineal gland, or spread from cancers primarily located in other organs (metastatic tumors).
Any brain tumor is inherently serious and life-threatening because of its invasive and infiltrative character in the limited space of the intracranial cavity. However, brain tumors (even malignant ones) are not invariably fatal. Brain tumors or intracranial neoplasms can be cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign); however, the definitions of malignant or benign neoplasms differs from those commonly used in other types of cancerous or non-cancerous neoplasms in the body. Its threat level depends on the combination of factors like the type of tumor, its location, its size and its state of development. Because the brain is well protected by the skull, the early detection of a brain tumor only occurs when diagnostic tools are directed at the intracranial cavity. Usually detection occurs in advanced stages when the presence of the tumor has caused unexplained symptoms.
Primary (true) brain tumors are commonly located in the posterior cranial fossa in children and in the anterior two-thirds of the cerebral hemispheres in adults, although they can affect any part of the brain.
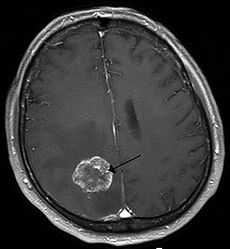 |
| Add caption |
Any brain tumor is inherently serious and life-threatening because of its invasive and infiltrative character in the limited space of the intracranial cavity. However, brain tumors (even malignant ones) are not invariably fatal. Brain tumors or intracranial neoplasms can be cancerous (malignant) or non-cancerous (benign); however, the definitions of malignant or benign neoplasms differs from those commonly used in other types of cancerous or non-cancerous neoplasms in the body. Its threat level depends on the combination of factors like the type of tumor, its location, its size and its state of development. Because the brain is well protected by the skull, the early detection of a brain tumor only occurs when diagnostic tools are directed at the intracranial cavity. Usually detection occurs in advanced stages when the presence of the tumor has caused unexplained symptoms.
Primary (true) brain tumors are commonly located in the posterior cranial fossa in children and in the anterior two-thirds of the cerebral hemispheres in adults, although they can affect any part of the brain.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)